Chapter 3 – Linking Learning Objectives, Pedagogies, and Technologies
Reading Reflection
- Differentiate types of learning objectives;
- Select an appropriate instructional strategy for a given learning objective;
- Identify the types of pedagogical approaches and associated technologies to suit particular types of learning.
- Provide advice on how to match types of pedagogical approaches and technologies to types of learning.
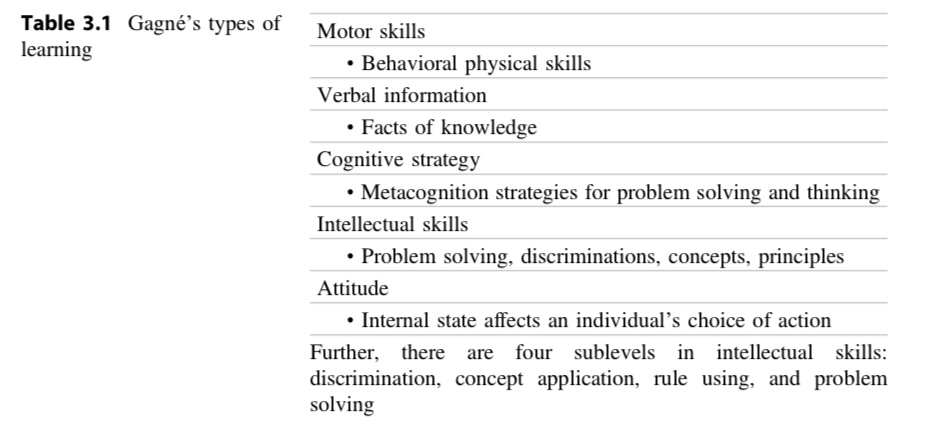
Types of learning:
“(a) verbal information (e.g., facts, as in knowing that), (b) cognitive strategies (e.g., selecting a process to address a problem situation, as in knowing why and when), (c) intellectual skills (e.g., using rules to solve a problem, as in knowing how), (d) motor skills (e.g., riding a bicycle, as in performing well), and (e) attitudes (e.g., fascination with science, as in being interested in or inclined to)” (Chapter 3, P50) and Table 3.1 (Chapter 3, P51).
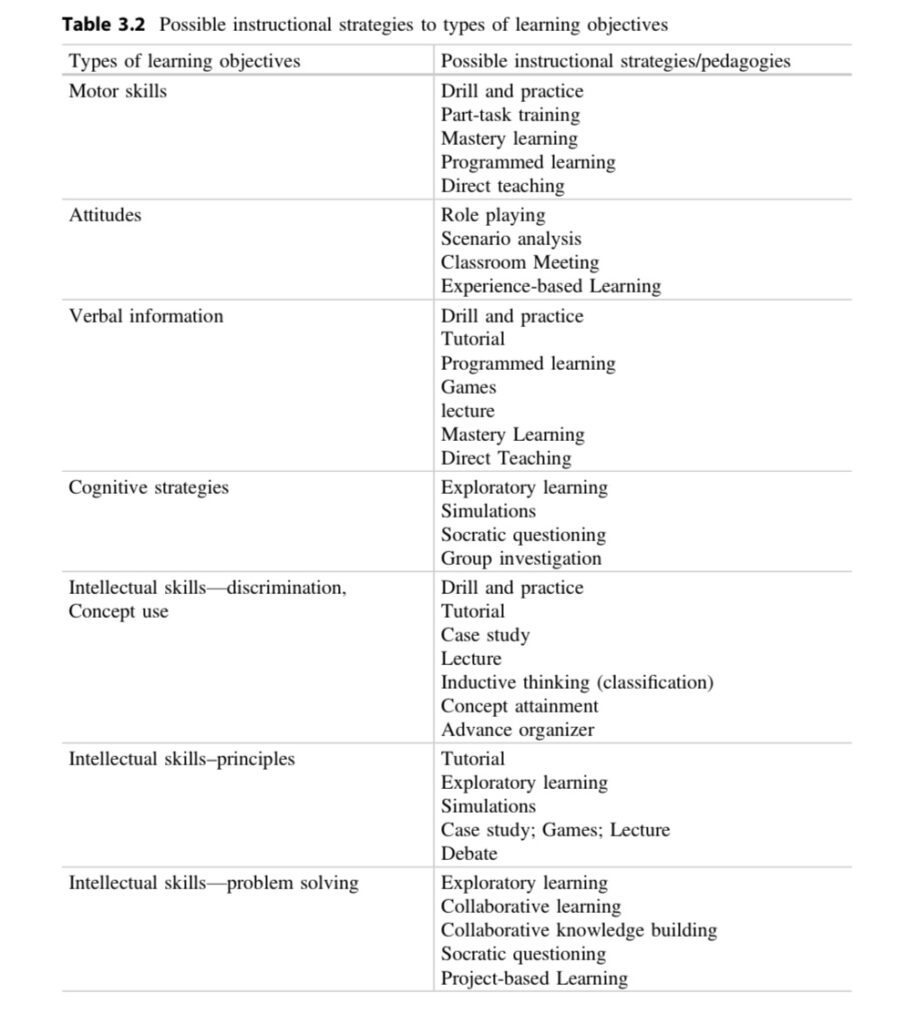
Appropriate instructional strategy:
“a. Drill and practice—appropriate for learning verbal information that for whatever reason must be committed to memory.
b. Tutorial instruction—appropriate for learning simple procedures or how to navigate within a particular software system.
c. Exploratory instruction—appropriate for promoting understanding about phenomena new to the learner.
d. Interactive simulation—appropriate for promoting critical reasoning about dynamic, complex systems.
e. Socratic questioning—appropriate for helping a learner link something new and seemingly unfamiliar to something already understood.
f. Lecture—appropriate for introducing a new topic and creating some motivation and an appropriate foundation for that topic.” (Chapter 3, P52&53).
The types of pedagogical approaches and associated technologies:
How to match types of pedagogical approaches and technologies to types of learning:
Some principles of multimedia learning and selection of technology for educational uses. a) Principle of Appropriateness; b) Principle of Authenticity; c) Principle of Cost; d) Principle of Interest; e) Principle of Organization and Balance (Mayer, Chapter 3, P60&61).
Learning Activities: Plan of teaching an 8-grade student about ocean tides.
First, analyze what type of knowledge is being taught. I consider ocean tides to be Cognitive strategies, so using Exploratory learning, Simulations, Socratic questioning, and Group investigation educational technology is helpful for students to learn. The specific steps to be implemented are described below.
Students are introduced to the topic of ocean tides before the class and research the knowledge on their own before the formal class. In the classroom, simulated scenarios are used to explain ocean tides and the teacher could use different technologies such as slides, videos, audio, animations, etc. Near the end of the class, Socratic questioning can be used, focusing on basic concepts, principles, theories, etc. The assignment can be a group activity to explore more about ocean tides.